| Type |
Features |
Uses |
|---|
| Paper 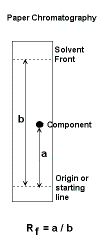
|
- inexpensive
- slow
- often used for water soluble compounds
- a qualitative technique
- stationary phase: usually water (present in the paper);
mobile phase:pure solvent or solvent mixture
- Retardation factor, Rf, measured
|
- identification of colours in inks or foods
- identification of amino acids
- separation of pigments in plant leaves
|
|
| Thin Layer (TLC) |
- inexpensive
- faster than paper and more sensitive
- used for less polar compounds
- qualitative technique although components may be scraped off the plate & their masses measured
- stationary phase: plate coated with silica gel or Al2O3;
mobile phase:pure solvent or solvent mixture
- Retardation factor, Rf, measured
|
- identification of biological sugars
- identifying components of pain-relieving preparations
- identifying components (eg, carboxylic acids) that might damage paper
|
|
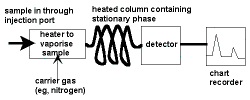
Gas
(GC, GLC) |
 area under the peak measures the amount of the component present area under the peak measures the amount of the component present |
- expensive
- fast
- used for gases or easily vaporised compounds
- relative molecular mass (Mr) < 300
- both qualitative and quantitative technique
- stationary phase: a liquid adsorbed onto an inert solid;
mobile phase (carrier gas): an inert gas such as helium, nitrogen
- Retention time, Rt, measured
|
- analysis of air-borne pollutants
- analysis of athletes' urine samples for performance enhancing drugs
- analysis of oil spills
- analysis of essential oils in perfume preparation
|
|
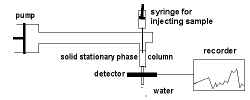
High-performance Liquid
(HPLC) |
 area under the peak measures the amount of the component present area under the peak measures the amount of the component present |
- expensive but less expensive than gas chromatography (GC)
- fast but slower than gas chromatography (GC)
- used for organic compounds that decompose if vaporised or compounds with relative molecular mass (Mr) > 300
- both a qualitative and a quantitative technique
- stationary phase: small waxy solids;
mobile phase (eluent): pure solvent or solvent mixture
- Retention time, Rt, measured
|
- analysis of pharmaceuticals
- cyanide analysis
- analysis of organic pollutants in water
- analysis of toxic compounds in shell fish
- protein analysis
|


 area under the peak measures the amount of the component present
area under the peak measures the amount of the component present area under the peak measures the amount of the component present
area under the peak measures the amount of the component present