Polythene (polyethylene):Properties, Production & Uses
Properties and Uses
| Property | Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) |
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | ~115oC | ~135oC |
| Crystallinity | low crystallinity (50-60% crystalline) Main chain contains many side chains of 2-4 carbon atoms leading to irregular packing and low crystallinity (amorphous) |
highly crystalline (>90% crystalline) contains less than 1 side chain per 200 carbon atoms in the main chain leading to long linear chains that result in regular packing and high crystallinity |
| Flexibility | more flexible than HDPE due to lower crystallinity | more rigid than LDPE due to higher crystallinity |
| Strength | not as strong as HDPE due to irregular packing of polymer chains | strong as a result of regular packing of polymer chains |
| Heat Resistance | retains toughness & pliabilty over a wide temperature range, but density drops off dramatically above room temperature. | useful above 100oC |
| Transparency | good transparency since it is more amorphous (has non-crystalline regions) than HDPE | less transparent than LDPE because it is more crystalline |
| Density | 0.91-0.94 g/cm3 lower density than HDPE |
0.95-0.97 g/cm3 higher density than LDPE |
| Chemical Properties | chemically inert Insolvent at room temperature in most solvents. Good resistance to acids and alkalis. Exposure to light and oxygen results in loss of strength and loss of tear resistance. |
chemically inert |
| Schematic diagram | 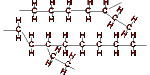 |
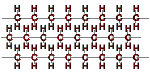 |
| Uses | sandwich bags, cling wrap, car covers, squeeze bottles, liners for tanks and ponds, moisture barriers in construction | freezer bags, water pipes, wire and cable insulation, extrusion coating |
