Monomer Name
Monomer Structure |
Polymer Name
Polymer Structure |
Polymer Uses |
|---|
ethene [ethylene]
CH2=CH2 |
polyethene [polythene or polyethylene, PE]
-(-CH2-CH2-)n- |
LDPE for sandwich wrap, cling wrap
HDPE for water pipes, wire insulation |
|
propene [propylene]
CH2=CHCH3 |
polypropene [polypropylene, PP]
-(-CH2-CHCH3-)n- |
electrical appliances, automotive applications, ropes, carpets, films |
|
chloroethene [vinyl chloride]
CH2=CHCl |
poly(vinyl chloride), PVC
-(-CH2-CHCl-)n- |
indoor electrical conduit, underground water pipes |
|
tetrafluoroethene [tetrafluoroethylene, teflon, PTFE]
CF2=CF2 |
polytetrafluorethene [polytetrafluoroethylene, teflon]
-[-CF2-CF2-]n- |
Insulation for wires, motors, generators, etc.
Anti-stick applications in cookware, bearings. |
|
styrene [vinyl benzene]
CH2=CH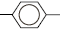 |
polystyrene
[poly(vinylbenzene), PS]H
|
-(C-
|
H | H
|
C-
|
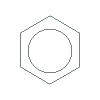 |
)n- |
|
heat and electrical insulation, pipes |
|
acrylonitrile [vinyl cyanide]
CH2=CH-CN |
polyacrylonitrile
-(-CH2-CHCN-)n- |
acrylic fabrics stronger than wool |
|
vinyl acetate
CH3COOCH=CH2 |
polyvinylacetate (PVA)
-(-CH3COOCH-CH2-)n- |
adhesives, paints |


