| Ksp |
|---|
| magnesium | calcium |
|---|
|
| carbonate | 3.5 x 10-8 | 2.8 x 10-9 |
|---|
|
| oxalate | 1.0 x 10-8 | 4.0 x 10-9 |
|---|
|
| fluoride | 6.5 x 10-9 | 4.0 x 10-11 |
|---|
|
| hydroxide | 1.8 x 10-11 | 5.0 x 10-6 |
|---|
Magnesium carbonate, oxalate and fluoride are all more soluble than calcium carbonate, oxalate and fluoride.
Magnesium hydroxide, however, is less soluble than calcium hydroxide.
It should be possible to precipitate magnesium hydroxide out of the water without precipitating out all the calcium as calcium hydroxide.
|
Mg(OH)2 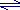 Mg2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) Mg2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)
Ksp(Mg(OH)2) =[Mg2+][OH-]2
1.8 x 10-11 = [Mg2+][OH-]2
Let y = [Mg2+] at equilibrium
Then [OH-] = 2y at equilibrium
So 1.8 x 10-11 = y x (2y)2
1.8 x 10-11 = y x 4y2
1.8 x 10-11 = 4y3
4.5 x 10-12 = y3
y = 1.65 x 10-4
[Mg2+] = 1.65 x 10-4 mol L-1
[OH-] = 2 x 1.65 x 10-4
= 3.30 x 10-4 mol L-1
|
Ca(OH)2  Ca2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) Ca2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)
Ksp(Ca(OH)2) =[Ca2+][OH-]2
5.0 x 10-6 = [Ca2+][OH-]2
Let y = [Ca2+] at equilibrium
Then [OH-] = 2y at equilibrium
So 5.0 x 10-6 = y x (2y)2
5.0 x 10-6 = y x 4y2
5.0 x 10-6 = 4y3
1.25 x 10-6 = y3
y = 1.08 x 10-2
[Ca2+] = 1.08 x 10-2 mol L-1
[OH-] = 2 x 1.08 x 10-2
= 2.16 x 10-2 mol L-1
|
Under the same conditions, the concentration of hydroxide ions in the calcium hydroxide solution is about 100 times more than the concentration of hydroxide ions in the magnesium hydroxide solution.
Calcium hydroxide is more soluble than magnesium hydroxide under the same conditions.
|
|

 Mg2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)
Mg2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq)